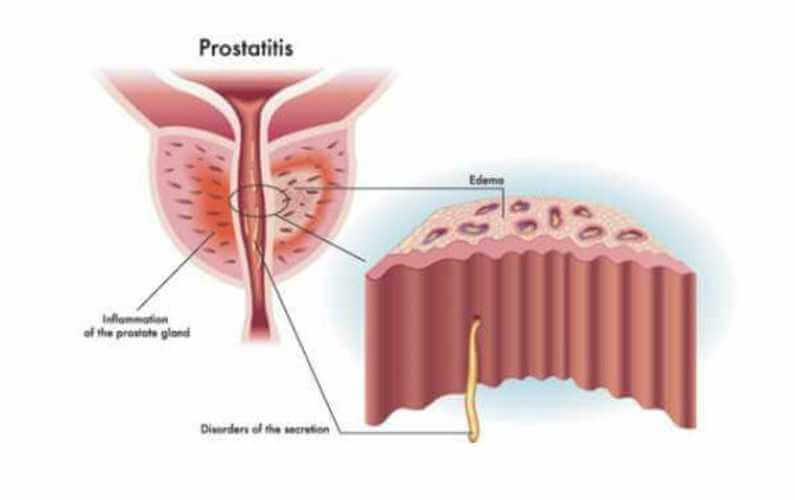
BLADDER CANCER
Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer forms in tissues of the bladder. Most bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas (cancer that begins in cells that normally make up the inner lining of the bladder). Other types include squamous cell carcinoma (cancer that begins in thin, flat cells) and adenocarcinoma (cancer that begins in cells that make and release mucus and other fluids). The cells that form squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma develop in the inner lining of the bladder as a result of chronic irritation and inflammation.

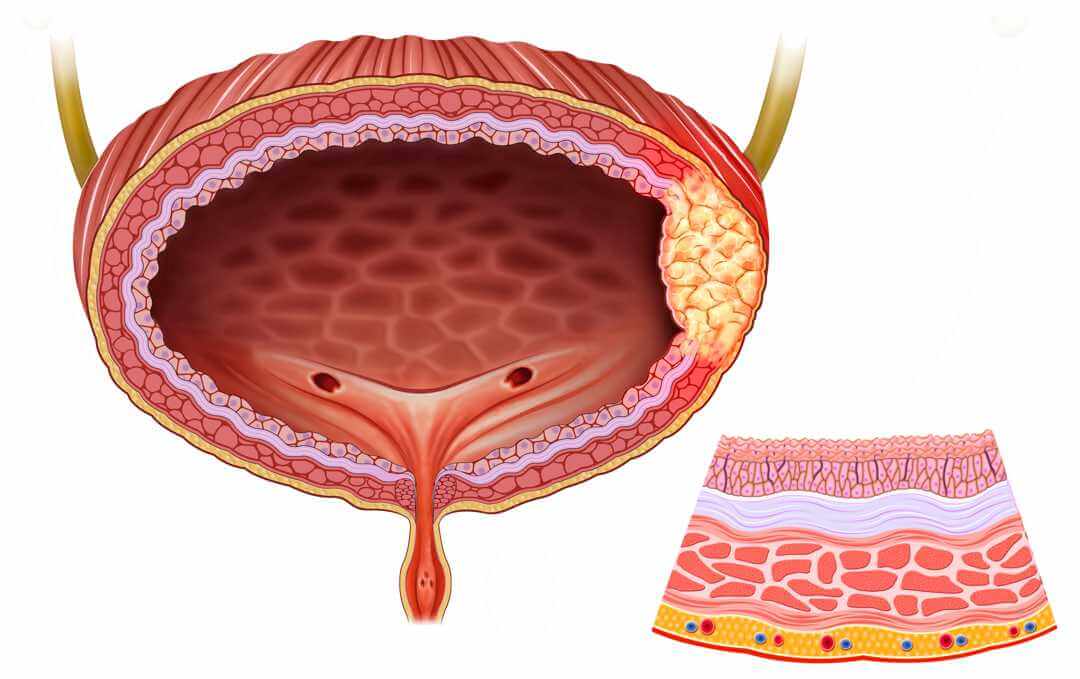
Common Symptoms
The most common presenting symptom is Gross Hematuria (gross blood in the urine) or irritative voiding symptoms such as urinary frequency and urgency. A Cystoscopy is performed in the office to confirm if a tumor is present in the bladder. A Bladder Biopsy is subsequently performed in the office or in a Surgery Center under Anesthesia to confirm a Bladder Cancer. At that time further treatment options can be undertaken depending on the grade and agressiveness of the tumor.